Guidelines to Write Eye-Catching Headings
January 18, 2022| Category: Writing Tips
If you write several pages of sheer text without headings, it will never work to your benefit. First of all, your readers will get bored too fast when trying to grasp the presented information. Secondly, if you are writing an academic essay or a blog article, it will look incomplete in terms of proper formatting. Hence, you need to provide logical headings to each separate part of your text.
Anyway, the aim of headings and subheadings is not only to make your written work esthetically pleasant. The main goal is to create a simplified navigation map between the parts of your piece, especially if this document is quite lengthy. Also, you have to face the fact, which writers usually find rather unfavorable, – only the minority of your target audience will read your paper from the start to finish. Therefore, your readers need headings to skip less interesting parts and concentrate on the most relevant information for them. Moreover, you have to remember that all headings have to create coherent connections between paragraphs. Even if they define separate parts, they still revolve around your principal subject.
It is also useful to check whether your headings reflect clarity. To do this, read the headings in sequence as if they represent your Table of Contents. Afterwards, ask yourself whether your prospective readers will be able to comprehend the following:
- The main idea of your written work.
- The contrasting content of each separate part.
- The connections between your sections and their embodiment of the focal points.
If you cannot firmly answer at least one of these questions, then you have to edit your headings and subheadings before submitting the final work.
The Difference between Headings and Titles
There is a difference between titles and headings, which may seem to be insignificant at first glance. A title indicates the major idea of the document and defines the most appropriate name for your subject matter. Typically, there cannot be many titles. In contrast, a heading labels only a specific chapter, revealing the main idea of the content written in a separate part. Usually, an academic text or a blog article consists of several part and has corresponding number of headings.
Can Headings Be Lengthy?
Generally, headings should not look like extensive sentences, if not like ordinary sentences at all. In some instances, you can create longer headings than usual if there is no other option to communicate the idea of the section. The primary goal of your heading is to unravel the key ideas of the information presented in that section. Still, you have to be careful not to break the rules of academic or literary concision. Do your best to shorten a lengthy heading to one line.
Two Types of Headings: Higher-Level and Lower-Level
When we talk about higher-level headings, we usually refer to single-word general technical headings such as Abstract, Introduction, Methodology, Literature Review, etc. It is common to use higher-level headings in academic papers. We do not commonly invent some alternative names for introductory or concluding parts. On the contrary, lower-level headings are aimed at elucidating the matter in question. Hence, you can make use of a subject-related terminology or other clarifying features, which reflect the content of the subsequent subsections.
The Usage of Headings to Describe Your Subject Matter
Brief unambiguous description of the investigated issue draws attention of the potential readers, especially if you present it wittily. It is beneficial to experiment with your headings to come up with the most suitable ones. Sometimes, it takes effort not to use cliches in your headings, but some alternative approaches can make your content unique. In any case, there should be a balance between uncliched phrases and relative simplicity. If you do not intend to write a highly complicated literary oeuvre, then highfalutin vocabulary will be totally inappropriate. Look at the examples of a non-descriptive heading and some succinct descriptive headings and see the difference for yourself.
Incorrect non-descriptive heading: TikTok
Correct descriptive headings:
- TikTok: Social Networking Service, which Changed the Digital World.
- From an Awkward Name to the Trendiest Game. “TikTok” History.
- How TikTok Influences the Intellectual Capacity of Modern Teenagers.
Further, you can find brief tips on creating the most effective headings.
Avoid repetition in headings
Of course, every writer understands that it would be strange to present two identical headings in one article. Yet, there have been frequent instances when headings for different paper parts sounded too similar. Always choose compelling but different words for each chapter.
Be careful with technical terms
If you write a paper based on technical terms, then it is difficult to avoid them in headings. Yet, it is wrong to satiate every new starting headline with complicated scientific terms. It is always more advantageous to keep a broader target audience in mind, not only technicians and scientists.
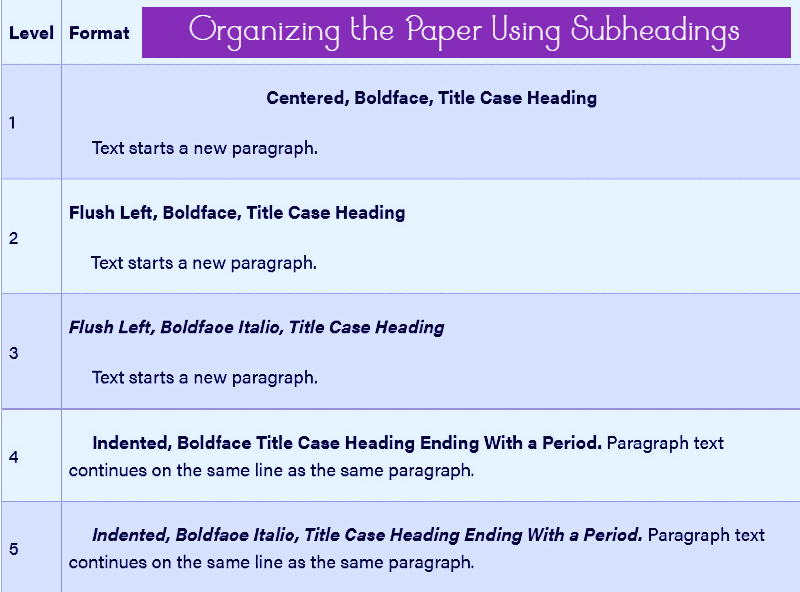
Capitalize and format your headings according to the rules
Remember that there may be different levels of headings. Heading levels should be formatted identically and consistently throughout the paper. Also, scrutinize the features of parallel structure.
Various academic writing styles offer slightly different requirements regarding capitalization, formatting, and sequencing of headings. Thus, you have to be fully aware of the differences between MLA headings, APA headings, Harvard headings, and Turabian headings.
Check academic formatting updates before selecting automatic heading styles
In order to simplify the process of formatting headings, many use automatic features, which can be quite brilliant in Google Docs and Microsoft Word. However, relying solely on automatic formatting features may lead to the unexpected failures because many colleges and universities constantly update their formatting requirements. The mentioned tools cannot predict those changes, so relying on preformatted headings can result in a surprising drawback rather than simplified process. For this reason, it is always wise to check the updates of formatting rules of the necessary educational establishment or updates in the formatting style.
